Confident Decisions Start with
Expert Financial Guidance
Confident Decisions
Start with
Expert Financial Guidance
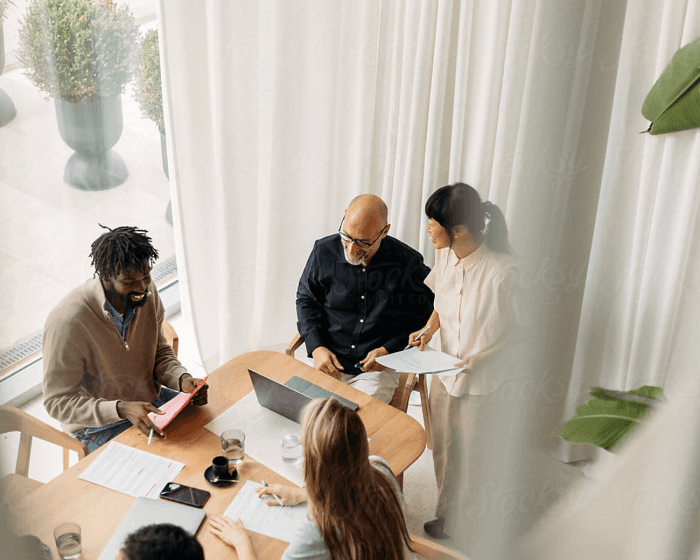
From startup to scale, CFO Share provides a consultative partnership that delivers the insights you need to understand your business, industry, and market.




Excellent communication
What use is an accountant who never responds to your emails? Our 24-hour responsiveness promise guarantees you will not be left waiting.

Excellent communication
What use is an accountant who never responds to your emails? Our 24-hour responsiveness promise guarantees you will not be left waiting.

Excellent communication
What use is an accountant who never responds to your emails? Our 24-hour responsiveness promise guarantees you will not be left waiting.

Excellent communication
What use is an accountant who never responds to your emails? Our 24-hour responsiveness promise guarantees you will not be left waiting.

Flexibility
No long-term contracts; we earn your business every month.

Flexibility
No long-term contracts; we earn your business every month.

Flexibility
No long-term contracts; we earn your business every month.

Flexibility
No long-term contracts; we earn your business every month.

Radical transparency
We earn your trust by giving you clear insight into the good and bad of your business, especially if it means owning a mistake we made.

Radical transparency
We earn your trust by giving you clear insight into the good and bad of your business, especially if it means owning a mistake we made.

Radical transparency
We earn your trust by giving you clear insight into the good and bad of your business, especially if it means owning a mistake we made.

Radical transparency
We earn your trust by giving you clear insight into the good and bad of your business, especially if it means owning a mistake we made.

Team approach
You get a team of financial specialists for less than the cost of one FTE

Team approach
You get a team of financial specialists for less than the cost of one FTE

Team approach
You get a team of financial specialists for less than the cost of one FTE

Team approach
You get a team of financial specialists for less than the cost of one FTE
Client testimonials
Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab
Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq
Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear
Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land

Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab

Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq

Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear

Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land

Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab

Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq

Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear

Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land

Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab

Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq

Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear

Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land

Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab
Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq
Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear
Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land

Joe Selvik
Co-Founder, FixturFab
Tatinana Finkelsteyn
CEO, Zlinq
Jessica Crothers
COO, Good Buy Gear
Nick Otis
Managing Member, Globeville Building and Land



Numbers That Speak for Themselves
Revenue under management and counting
Explore practical insights designed to transform your financial strategies and unlock new opportunities.
Seamlessly integrated finance to unlock growth.
Want to learn more? Schedule a call to meet with our team.












